
The Income Tax Act of 1961 is one of the most important legislative tools used to ensure tax compliance and governance in India. Among the various provisions under this Act, Section 194J plays a crucial role in regulating the Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on payments made for professional or technical services. As businesses increasingly turn to freelancers, consultants, and other professionals, understanding the taxation of professional fees has become vital for both payers and payees.
We will provide an in-depth understanding of these sections, the threshold limits, exemptions, and penalties for non-compliance. This guide will also help businesses understand their responsibilities regarding TDS under these sections. Additionally, we will address the FAQs and provide the latest updates on these provisions.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Section 194J
- Key Features of Section 194J
- What Does Section 194J of the Income Tax Act Cover?
- TDS on Professional and Consultancy Fees: In Detail
- Understanding the TDS Limit and Threshold for Section 194J
- The Concept of Section 194JB and Section 194JA
- TDS on Software Purchase Under Section 194J
- How to Deduct and Deposit TDS Under Section 194J
- Compliance and Filing TDS Returns
- Penalties for Non-Compliance Under Section 194J
- Practical Scenarios for Section 194J
- Important Differences Between Section 194J, 194JB, and 194JA
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Latest Updates and Changes Regarding Section 194J
- Conclusion
- References
1. Introduction to Section 194J
Section 194J of the Income Tax Act, 1961 mandates the deduction of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) on certain payments made to professionals and technical experts. The section primarily focuses on payments made for professional services, technical services, royalties, and fees for the use of technical or professional services. The government introduced this section to bring various freelance or consultancy-based services into the tax net and improve the overall tax collection process.
Section 194J ensures that the payer (often businesses or individuals hiring professionals) is responsible for deducting a certain percentage of tax from the payment made to the professional service provider and depositing it with the Income Tax Department. The payee, the professional, can later claim this TDS as a credit while filing their income tax returns.
2. Key Features of Section 194J
- Scope of Application: This provision applies to a variety of professional and technical services, including but not limited to consultancy services, legal services, technical services, royalties, and fees for the use of intellectual property rights.
- TDS Rate: The rate of TDS under Section 194J is typically 10%, but it can vary depending on the nature of the payment.
- Threshold Limit: TDS is applicable only when the payment for such services exceeds a certain threshold limit. For professional and technical fees, the limit is ₹30,000.
- Exemption for Resident Individuals and HUF: If the payment is made to a resident individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF), the TDS provisions may not apply if the recipient’s total income is below the taxable threshold.
3. What Does Section 194J of the Income Tax Act Cover?
Section 194J broadly covers the following types of payments:
A. Professional Services
These include services offered by professionals such as:
- Consultants: Offering advice, guidance, or expertise in various industries such as marketing, finance, etc.
- Legal Services: Payments made to lawyers, legal advisors, and related services.
- Accountancy Services: Services provided by chartered accountants, auditors, etc.
- Technical Services: Any service involving the use of specialized technical knowledge, including software development, design, and technical consultancy.
B. Technical Services
Technical services are services that involve engineering or scientific expertise, including but not limited to:
- Software development and installation
- Engineering consultancy
- Design and development of technical solutions
C. Royalty and Use of Intellectual Property Rights
Payments made for the use of patents, copyrights, trademarks, and other intellectual property rights are also covered under Section 194J.
4. TDS on Professional and Consultancy Fees: In Detail
When businesses hire professionals such as consultants, lawyers, and auditors, they are required to deduct TDS at the rate of 10% if the payment exceeds the threshold limit of ₹30,000 in a financial year. Let’s look at how this works:
- Example 1: A company hires a consultant for ₹50,000 for a project.
- TDS of ₹5,000 (10% of ₹50,000) is deducted by the company and deposited with the government.
- Example 2: A legal firm provides legal consultancy services for ₹25,000.
- No TDS is deducted because the payment is below ₹30,000.
TDS on Professional Fees
Professional fees include the payments made to doctors, architects, lawyers, engineers, and other such professionals who render specialized services.
5. Understanding the TDS Limit and Threshold for Section 194J
TDS Limit Under Section 194J
The threshold limit for TDS deduction under Section 194J is ₹30,000 in a financial year for professional and technical services. This means that if a business pays ₹30,000 or less to a professional for services, no TDS is required to be deducted. However, if the payment exceeds ₹30,000, TDS will be deducted at the rate of 10% (for residents).
- Threshold Limit for Professional Fees: ₹30,000 per annum.
- TDS Rate: 10% for professionals providing services.
This threshold applies to payments made for professional services like consultancy fees, legal fees, technical services, and other specified services under the Income Tax Act.
6. The Concept of Section 194JB and Section 194JA
Along with Section 194J, there are also related sections such as 194JB and 194JA which have distinct purposes but are closely related to the taxation of professional and technical fees.
Section 194JB of the Income Tax Act
Section 194JB specifically deals with the deduction of tax on payments made for royalties and fees for technical services. It applies in a similar manner as Section 194J but is typically used for payments to foreign entities or payments that involve the use of intellectual property rights.
Section 194JA of the Income Tax Act
Section 194JA deals with the deduction of tax on fees paid for technical services that are provided by professionals who are in the business of providing services related to information technology. The TDS rate under Section 194JA is usually lower, depending on the type of service provided.
7. TDS on Software Purchase Under Section 194J
When purchasing software or paying for software-related services, Section 194J may come into play. For example, if a company buys software from a foreign vendor or a domestic company, TDS is applicable on payments exceeding the threshold of ₹30,000.
This includes payments made for software licensing, royalty payments for using software, or maintenance contracts. These are considered technical services under Section 194J.
Example:
- A company purchases licensed software for ₹40,000.
- The company needs to deduct ₹4,000 as TDS (10% of ₹40,000) and deposit it with the government.
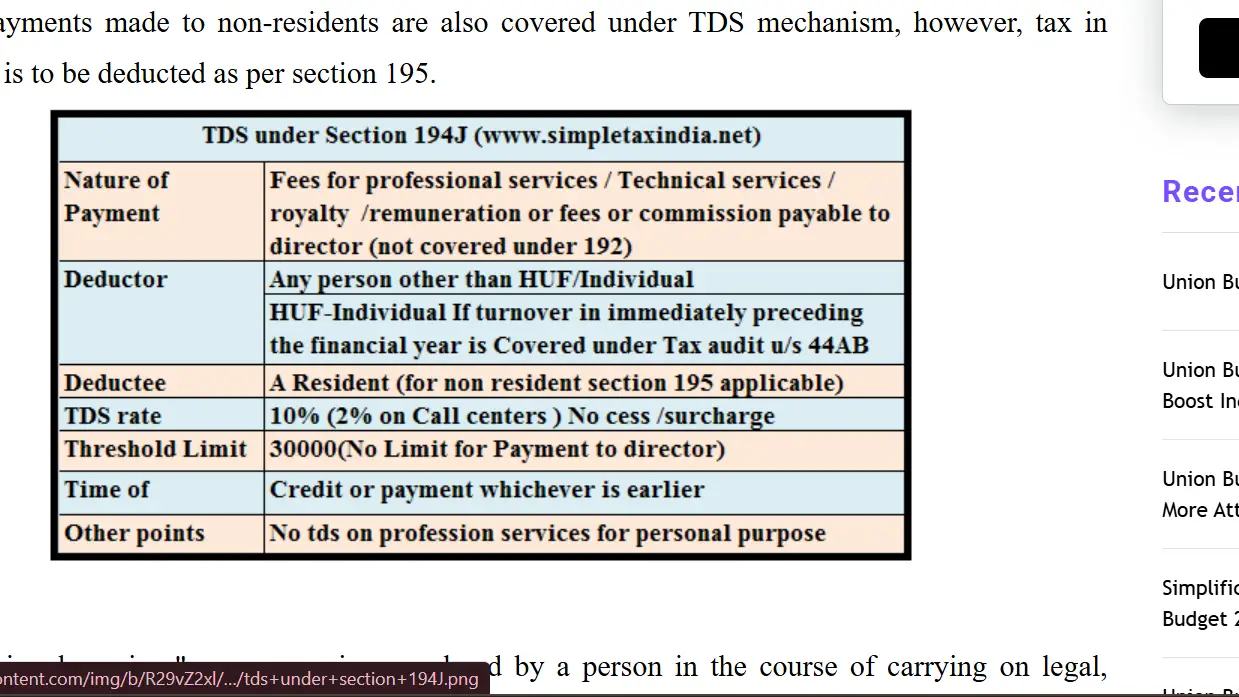
P.C. – simpletaxindia.net
8. How to Deduct and Deposit TDS Under Section 194J
Steps to Deduct TDS Under Section 194J:
- Identify the Payment: Determine if the payment made to a professional or technical consultant exceeds ₹30,000.
- Calculate the TDS: If the payment exceeds the limit, deduct 10% of the payment as TDS.
- Deposit the TDS: The deducted TDS should be deposited with the government by using the appropriate challan.
- File TDS Returns: File the TDS returns using Form 26Q and provide details of the TDS deducted and deposited.
9. Compliance and Filing TDS Returns
TDS returns need to be filed regularly, typically on a quarterly basis. For businesses and individuals deducting TDS under Section 194J, it’s important to follow the correct procedure for deposit and filing to avoid penalties. Returns can be filed through the TRACES portal, and the Form 26Q must be used to report the deducted TDS.
10. Penalties for Non-Compliance Under Section 194J
Failure to comply with the TDS requirements under Section 194J can result in penalties, including:
- Interest: If the TDS is not deposited on time, interest will be charged on the amount of tax that was not paid on time.
- Penalty for Non-Deduction: If no TDS is deducted, a penalty of ₹100 per day may be imposed, up to the amount of TDS that was to be deducted.
11. Practical Scenarios for Section 194J
Here are a few practical examples to better understand how Section 194J works:
Example 1: Consultancy Fees
A company hires a consultant for a one-time project, and the payment made is ₹40,000. Since this is over ₹30,000, the company must deduct ₹4,000 as TDS (10%) and remit it to the government.
Example 2: Legal Fees
A company hires a lawyer for legal advice and the total payment is ₹25,000. In this case, no TDS is required as the payment is below the threshold of ₹30,000.
12. Important Differences Between Section 194J, 194JB, and 194JA
Although Section 194J, 194JB, and 194JA are related in the context of TDS on professional and technical fees, they serve distinct purposes:
- Section 194J: TDS on professional and technical services, including consultancy fees and legal fees.
- Section 194JB: TDS on payments related to royalties and technical services provided by foreign entities.
- Section 194JA: TDS on fees paid for technical services such as IT consultancy.
13. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is Section 194J of the Income Tax Act?
- Section 194J mandates TDS on professional and technical services, including consultancy fees.
- What is the TDS rate under Section 194J?
- The TDS rate is generally 10%.
- Is TDS applicable on payments to professionals?
- Yes, TDS is applicable when payments to professionals exceed ₹30,000 in a financial year.
- What is Section 194JB?
- Section 194JB deals with TDS on royalties and technical services provided by foreign entities.
- When is TDS deducted on professional fees?
- TDS is deducted when the payment exceeds ₹30,000.
- How is TDS on consultancy services calculated?
- TDS is calculated at 10% of the amount paid to the consultant exceeding ₹30,000.
- Is TDS applicable on payments made for software?
- Yes, TDS is applicable when purchasing software, especially if the payment exceeds ₹30,000.
- What happens if TDS is not deducted?
- A penalty and interest will be imposed for non-deduction of TDS.
- Do freelancers need to pay TDS under Section 194J?
- Yes, freelancers receiving payments over ₹30,000 will have TDS deducted by the payer.
- What is the filing procedure for TDS under Section 194J?
- TDS returns must be filed using Form 26Q.
14. Latest Updates and Changes Regarding Section 194J
As per the latest updates in the Finance Act 2023, no major amendments have been made to Section 194J, and the TDS rate remains at 10%. However, there are updates regarding compliance deadlines, which are subject to government notifications.
15. Conclusion
Section 194J is an essential provision for TDS on payments made for professional and technical services, ensuring that a broader tax base is created. Understanding the application of TDS on professional and consultancy fees can help businesses stay compliant with the Income Tax Act.
This detailed guide has covered everything you need to know about Section 194J, 194JB, and 194JA, including threshold limits, TDS rates, and the filing procedures. By following the rules and ensuring timely deductions, businesses can avoid penalties and contribute to the nation’s tax base effectively.
16. References
- Income Tax Act, 1961: Income Tax India
- ClearTax Overview on Section 194J: ClearTax
- IndiaFilings on Section 194J: IndiaFilings
Also Read: Understanding Section 194Q of the Income Tax Act: A Comprehensive Guide
Also visit: Online Legal Service, Virtual Advice and Consultation
Also Read: Section 80EEA: A Detailed Guide to Home Loan Tax Deductions
Also Read: Understanding the Income Tax Act of 1961: Recent Updates, Amendments, and Key Insights



