
Cyber crimes in India are on the rise, posing a significant threat to individuals, businesses, and government institutions. With the rapid increase in internet usage, cybercriminals are finding new ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Understanding the top cyber crimes in India and knowing how to protect yourself can help you stay safe online. This blog will explore the top 10 cyber crimes in India and provide practical tips on how consumers can protect themselves.
Table of Contents
1. Phishing Attacks
Phishing is a common cybercrime where criminals send fraudulent emails or messages to trick individuals into revealing personal information such as passwords, credit card numbers, or bank account details. These messages often appear to come from legitimate sources.
How to Protect Yourself:
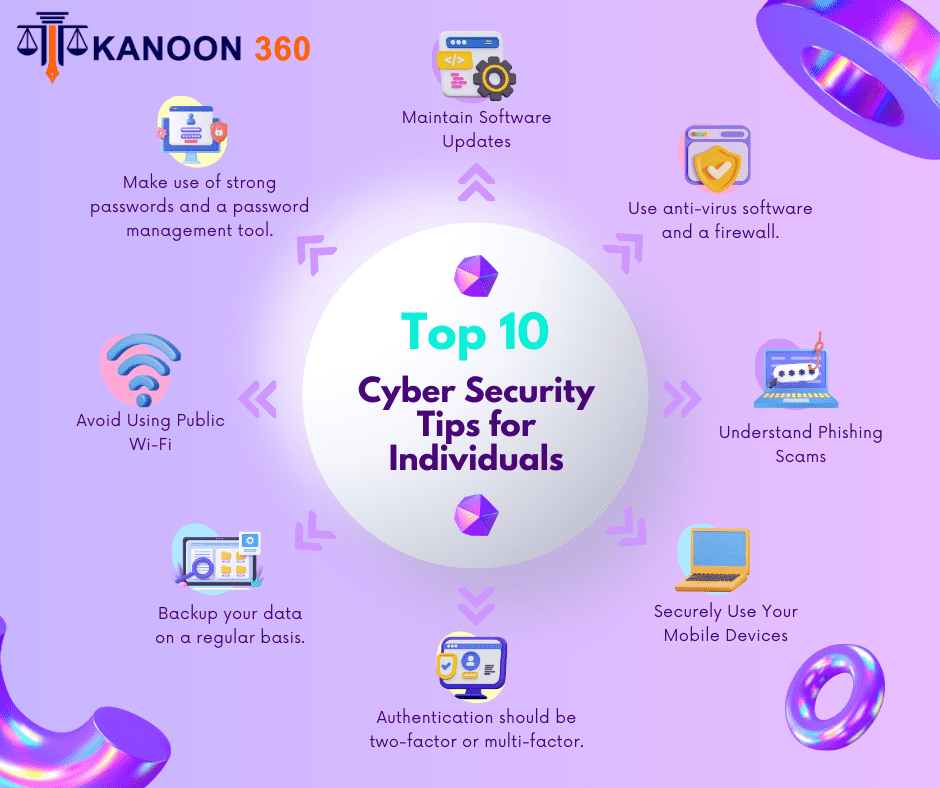
- Do not click on links or download attachments from unknown or suspicious emails.
- Verify the sender’s email address.
- Use two-factor authentication for your accounts.
2. Online Banking Fraud
Online banking fraud involves unauthorized transactions made using an individual’s bank account information. This can happen through phishing attacks, malware, or unauthorized access to banking credentials.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Regularly monitor your bank statements for unauthorized transactions.
- Use strong, unique passwords for online banking.
- Enable transaction alerts to receive notifications for any activity on your account.
3. Identity Theft
Identity theft occurs when someone steals your personal information to commit fraud. This can include using your name, credit card number, or other personal details to make unauthorized purchases or open new accounts.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Shred documents containing personal information before disposing of them.
- Regularly check your credit reports for suspicious activity.
- Be cautious when sharing personal information online or over the phone.
4. Cyberstalking
Cyberstalking involves using the internet to harass or stalk someone. This can include sending threatening messages, spreading false information, or monitoring someone’s online activities without their consent.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Do not share personal information on social media.
- Use privacy settings to control who can see your online activities.
- Report any suspicious or threatening behavior to the authorities.
5. Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts a victim’s files, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. This can cause significant disruption and financial loss.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Regularly back up your important files.
- Use reputable antivirus software and keep it updated.
- Do not click on suspicious links or download attachments from unknown sources.
6. Social Engineering
Social engineering involves manipulating individuals into divulging confidential information. This can include impersonating a trusted individual or organization to gain access to sensitive information.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Be cautious of unsolicited requests for personal information.
- Verify the identity of the person or organization before sharing any information.
- Educate yourself about common social engineering tactics.
7. Credit Card Fraud
Credit card fraud involves unauthorized use of someone’s credit card information to make purchases or withdraw money. This can happen through skimming, phishing, or hacking.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Use credit cards with chip technology.
- Regularly monitor your credit card statements.
- Report lost or stolen credit cards immediately.
8. Child Exploitation
Child exploitation involves using the internet to exploit children for sexual or financial gain. This can include grooming, producing and distributing child pornography, or coercing children into illegal activities.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Educate your children about online safety.
- Monitor your children’s online activities.
- Report any suspicious behavior to the authorities.
9. Cyberbullying
Cyberbullying involves using digital platforms to harass, threaten, or intimidate someone. This can have serious emotional and psychological effects on the victim.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Do not engage with cyberbullies.
- Use privacy settings to limit who can contact you online.
- Report any instances of cyberbullying to the platform and the authorities.
10. Data Breaches
Data breaches occur when unauthorized individuals gain access to sensitive information stored by an organization. This can include personal information, financial data, or confidential business information.
How to Protect Yourself:
- Use strong, unique passwords for different accounts.
- Enable two-factor authentication.
- Regularly monitor your accounts for suspicious activity.
Legal Framework in India
India has implemented several laws and regulations to combat cybercrime, including the Information Technology Act, 2000, and the Indian Penal Code. These laws provide a legal framework for prosecuting cybercriminals and protecting individuals’ rights.
Reporting Cyber Crimes in India
If you fall victim to a cyber crime, it is crucial to report it to the appropriate authorities. The Government of India has established a dedicated cyber crime reporting portal: cybercrime.gov.in. This portal allows individuals to report various types of cyber crimes, including online harassment, financial fraud, and identity theft.
Don’t accept injustice just because the opponent is powerful! Take charge with Kanoon 360, the quickest & easiest Consumer Forum for consumer complaints in India. Visit our website or contact us today!
Also Read: Emerging Trends in Cyber Crime: What Indian Consumers Should Watch Out For
Also Read: How to Join Support Groups for Victims of Cyber Crime in India
Conclusion
Cyber crimes in India are evolving, making it essential for consumers to stay informed and take proactive steps to protect themselves. By understanding the top cyber crimes and following the practical tips provided, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to these malicious activities. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and stay safe online.
References
- “Phishing Attacks and How to Protect Yourself,” CERT-In, cert-in.org.in.
- “Online Banking Fraud: Tips to Stay Safe,” RBI, rbi.org.in.
- “Identity Theft: Prevention and Response,” Ministry of Home Affairs, cybercrime.gov.in.
- “Cyberstalking: Legal Measures and Protection,” National Crime Records Bureau, ncrb.gov.in.
- “Ransomware: How to Protect Your Data,” Data Security Council of India, dsci.in.
- “Social Engineering: Awareness and Defense,” CERT-In, cert-in.org.in.
- “Credit Card Fraud: Detection and Prevention,” NPCI, npci.org.in.
- “Child Exploitation: Online Safety for Children,” Ministry of Women and Child Development, wcd.nic.in.
- “Cyberbullying: How to Handle Online Harassment,” Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, meity.gov.in.
- “Data Breaches: Protection and Response,” CERT-In, cert-in.org.in.



