
The Employees’ State Insurance (ESI) scheme is a social security initiative introduced by the Indian government to provide comprehensive medical and financial support to workers and their families. The ESI Act, 1948, governs this scheme, ensuring that employees, especially those in the organized sector, have access to healthcare services, sickness benefits, maternity benefits, and more, during times of need. Understanding the ESI contribution, its rate, limits, eligibility, and more is crucial for both employees and employers.
Table of Contents
What is ESI Contribution?
ESI contribution is the amount paid by both employees and employers under the Employees’ State Insurance Act, 1948. The contribution helps fund a welfare program that provides social security benefits such as medical care, sickness benefits, maternity benefits, and disability pensions. These benefits are provided to employees in case of illness, injury, maternity, or death due to work-related accidents.
Both the employee and employer contribute to the ESI fund, and the amount is based on the employee’s salary. The funds collected through this contribution are managed by the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC), which operates under the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Key Aspects of ESI Contribution
1. ESI Contribution Rate
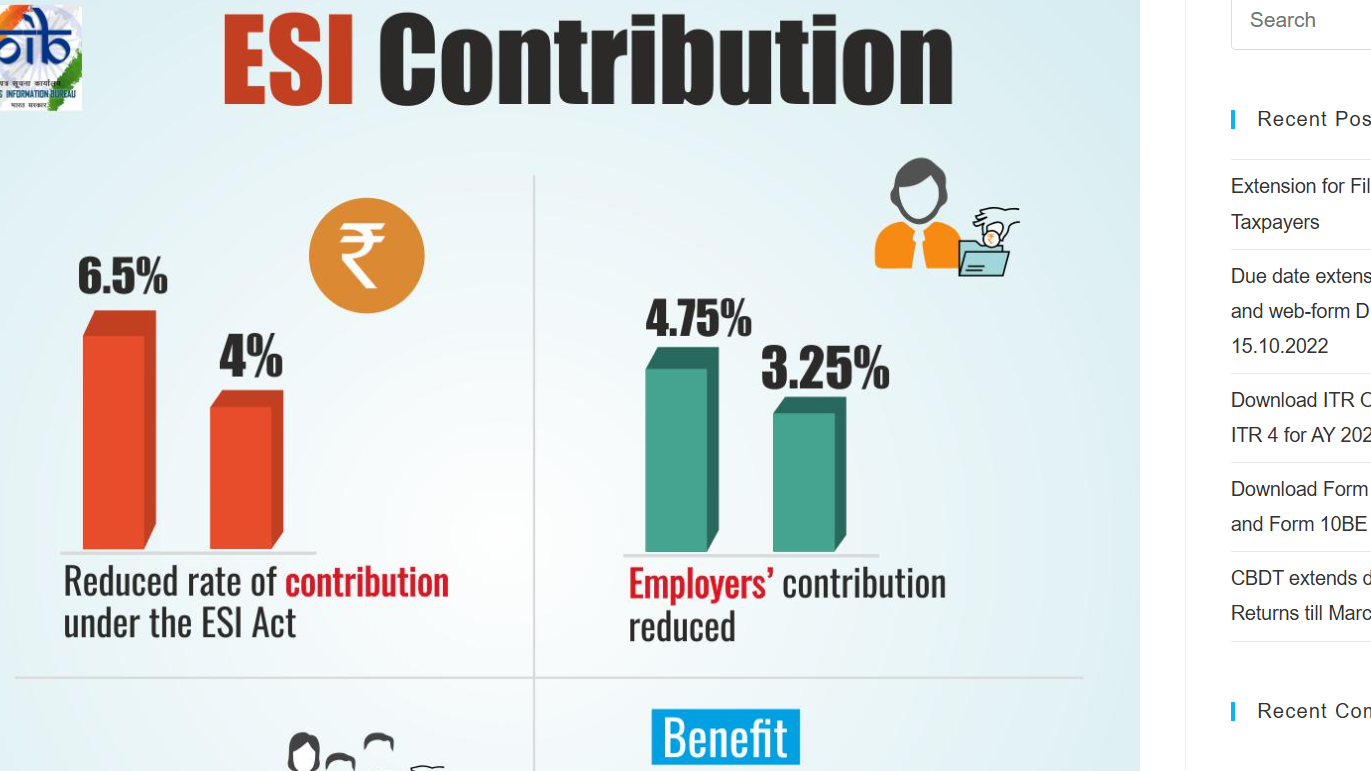
The ESI contribution rate is divided into two parts: the employee’s share and the employer’s share.
- Employee’s Share: The employee contributes 0.75% of their monthly salary towards ESI.
- Employer’s Share: The employer contributes 3.25% of the employee’s salary towards the ESI fund.
So, the total ESI contribution rate stands at 4% of the employee’s gross salary. The employer’s contribution is higher than the employee’s, which is why the employer plays a significant role in this system.
2. ESI Contribution Salary Limit
The ESI scheme applies to employees who are earning a monthly salary up to a certain limit. As per the latest regulations, the ESI contribution applies to employees earning a salary of up to ₹21,000 per month.
For employees with disabilities, the salary limit is higher, set at ₹25,000 per month. These limits are subject to change based on government notifications and revisions made by the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
Note: The salary is calculated on the basis of the total earnings, including basic salary, allowances, and other components.
3. ESI Contribution Percentage
As mentioned earlier, the total ESI contribution percentage is 4% of the employee’s monthly salary, with 0.75% being deducted from the employee’s salary and the remaining 3.25% being contributed by the employer. However, in cases where the employer’s contribution exceeds the prescribed limits, they can seek exemptions or adjustments as per applicable rules.
4. ESI Employee and Employer Contribution
- Employee Contribution: 0.75% of the employee’s gross salary.
- Employer Contribution: 3.25% of the employee’s gross salary.
Example: If an employee’s monthly salary is ₹20,000:
- The employee would contribute ₹150 (0.75% of ₹20,000).
- The employer would contribute ₹650 (3.25% of ₹20,000).
Thus, the total ESI contribution would be ₹800.
5. ESI Contribution Period
The ESI contribution is generally made on a monthly basis. Both the employee and employer are required to remit their contributions by the 15th of each month. This system helps ensure that employees receive timely access to their entitled benefits.
In cases where employees are hired or terminated mid-month, the contribution period may vary slightly, but employers are still responsible for ensuring the employee’s coverage under the scheme for the period of employment.
6. ESI Benefits
Employees covered under the ESI scheme are entitled to the following benefits:
- Medical Care: Employees and their families are entitled to medical care at ESIC hospitals and dispensaries.
- Sickness Benefit: Employees are entitled to cash benefits for up to 91 days in case of sickness.
- Maternity Benefits: Female employees are entitled to maternity benefits, which includes paid leave for a certain period.
- Disability Benefits: Employees who are injured at work or suffer from a work-related disability are entitled to compensation.
- Pension for Dependent Family Members: In case of the death of the insured employee, their dependents receive a pension.
7. Exemptions from ESI
Not all employees are covered under the ESI scheme. Some exemptions are as follows:
- Employees working in establishments with fewer than 10 employees.
- Employees earning above the ESI contribution salary limit (₹21,000 or ₹25,000, depending on the case).
- Some categories of workers, like seasonal workers or those employed in casual or irregular work, might not be included.
8. ESI Registration Process
For employers who are eligible under the ESI Act, the first step is registration with the Employees’ State Insurance Corporation (ESIC). The process involves:
- Filling out an online registration form on the ESIC portal.
- Providing required documents like proof of establishment, employee details, and more.
- Once registered, the employer is assigned a unique ESI code, which they need to use for filing contributions and claims.
9. ESI Filing & Payment Process
Employers are required to file ESI returns on a monthly basis. They must:
- Submit a detailed return of employees covered under ESI.
- Deposit the monthly contributions within the prescribed deadline.
- Maintain records for auditing purposes.
Latest Updates on ESI Contributions
In 2023, the Indian government made several amendments to the ESI rules and benefits. Some of the key updates are:
- Salary Limit: The salary limit for coverage under the ESI scheme was increased from ₹15,000 to ₹21,000 per month, with a higher limit of ₹25,000 for disabled employees.
- Medical Benefits: The government enhanced medical benefits by improving the facilities at ESIC hospitals and clinics.
- Online Services: The ESIC website has introduced online platforms for filing contributions, submitting claims, and tracking the status of benefits, making it more accessible for employers and employees.
For more information, you can visit the official ESIC website here.
P.C. – pstaxconsultancy.com
10 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on ESI Contributions
- What is ESI? ESI (Employees’ State Insurance) is a government welfare program providing healthcare and social security benefits to employees working in India. It includes benefits for medical care, sickness, maternity, and disabilities.
- How much is the ESI contribution? The total ESI contribution is 4% of the employee’s salary. The employee contributes 0.75%, and the employer contributes 3.25%.
- What is the ESI salary limit for 2025? The ESI salary limit is ₹21,000 per month. For employees with disabilities, the limit is ₹25,000 per month.
- What is the ESI contribution period? The ESI contribution is made monthly, and the payment must be made by the 15th of each month.
- Who is eligible for ESI? Employees working in establishments with more than 10 employees and earning up to ₹21,000 per month are eligible for ESI coverage.
- What benefits does ESI provide to employees? ESI provides medical care, sickness benefits, maternity benefits, disability benefits, and pensions to the family members of the deceased employee.
- How do I register for ESI? Employers must register with the ESIC portal by submitting the required details and documents to obtain an ESIC registration number.
- How can I file ESI returns? ESI returns can be filed online through the ESIC portal. Employers must provide employee details and make the contributions as per the prescribed rate.
- Can I opt out of ESI? If you are earning above the salary limit or work in a non-ESI-eligible establishment, you may not need to contribute. However, opting out of ESI for employees earning below the salary limit is not possible.
- Can an employer claim ESI benefits for employees? Yes, employers are responsible for ensuring their employees are enrolled under the ESI scheme and that benefits are made available in case of medical emergencies, injuries, or other qualifying situations.
Conclusion
The ESI scheme is a vital social security mechanism that provides essential benefits to employees, especially in times of sickness, injury, or maternity. Understanding the contribution rates, eligibility, and procedures is critical for both employers and employees to ensure that the benefits are maximized.
For both employers and employees, keeping up with the latest developments and ensuring timely registration, contribution filing, and claim submissions is essential for smooth operation.
To stay updated, regularly check the official ESIC website and follow government notifications related to ESI.
Also Read: Understanding YouTube Disclaimers: A Comprehensive Guide
Also Read: Understanding E-Way Bill Limit: A Comprehensive Guide
Also visit: Online Legal Service, Virtual Advice and Consultation
Also Read: Lakshmi Bhandar Scheme: Empowering Women in West Bengal with Financial Support



