
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) has brought about a major transformation in the way businesses manage and pay taxes in India. One of the essential aspects of the GST regime is the e-way bill, which facilitates the movement of goods between various locations while ensuring tax compliance. The e-way bill limit determines the circumstances under which an e-way bill must be generated, as well as the process for doing so. Understanding the e-way bill limit is crucial for businesses to remain compliant and avoid penalties, especially considering the latest updates regarding the e-way bill limit.
Table of Contents
What is an E-Way Bill?
An e-way bill is an electronic document generated on the e-way bill portal (www.ewaybill.nic.in) that authorizes the movement of goods from one place to another. Under the GST regime, businesses must generate an e-way bill whenever they transport goods that meet certain conditions related to value and distance. The e-way bill serves as a proof of compliance with the provisions of the GST Act and ensures that goods in transit are not evading tax.
The e-way bill system was introduced to prevent tax evasion and to streamline the transportation of goods across India. It helps businesses, transporters, and authorities track goods on their journey, ensuring smoother and transparent trade operations.
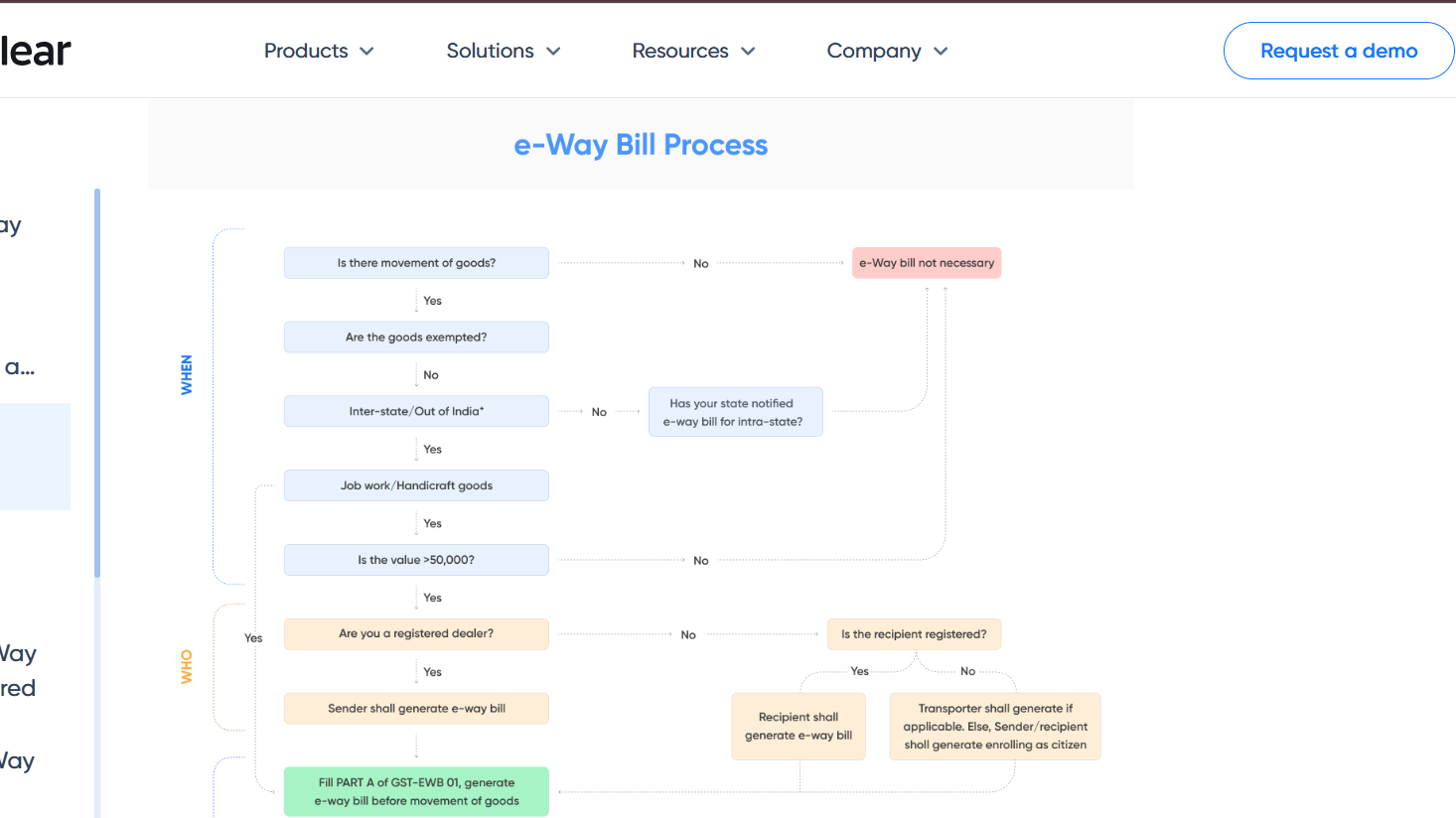
When is an E-Way Bill Required?
It is important to know the e-way bill limit as it impacts the logistics and cost of transportation for businesses. Businesses should regularly review their operations to ensure they operate within these limits.
According to the GST Act, an e-way bill is required under the following circumstances:
- Value of Goods: The value of goods being transported exceeds ₹50,000.
- Inter-State Movement: The goods are being transported from one state to another (inter-state movement).
- Intra-State Movement: Certain states also mandate the generation of e-way bills for intra-state transportation of goods exceeding the limit.
- Supply of Goods: When goods are being transported as part of a supply (including sales, return, or stock transfers).
However, there are exceptions to this rule, such as transportation of goods by rail, air, or vessels, where specific guidelines apply. Additionally, goods that are not taxable or exempt from GST are generally not subject to e-way bill generation.
Understanding EWay Bill Limit
The e-way bill limit refers to the monetary threshold value of goods being transported, which triggers the requirement for generating an e-way bill. As per the GST Act, businesses are required to generate an e-way bill if the total value of goods exceeds ₹50,000. This is the standard e-way bill limit for interstate and intrastate goods transportation.
Key points about the e-way bill limit:
- Threshold: The threshold limit of ₹50,000 is applicable to goods being moved across state borders or within a state in certain circumstances.
- Multiple Goods: If a consignment contains multiple goods, the aggregate value of the entire consignment determines whether an e-way bill must be generated.
- Transportation Mode: If goods are transported via road, rail, air, or ship, the e-way bill must be generated once the limit is crossed.
- Overloaded Vehicles: Even if the value of individual items in a consignment does not exceed ₹50,000, but the combined value of the consignment exceeds ₹50,000, an e-way bill will still be required.
How to Generate an E-Way Bill
To generate an e-way bill, businesses need to access the e-way bill portal (www.ewaybill.nic.in), which is the official government platform for e-way bill management. The steps to generate an e-way bill are as follows:
- Log In to the Portal: To start, you need to visit the e-way bill portal (www.ewaybill.nic.in) and log in using your GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) and other credentials.
- Enter the Details: Fill out the necessary details of the consignment, including the GSTIN of the sender and recipient, transport mode, transporter details, and the value of the goods being transported.
- Generate E-Way Bill: Once the details are filled out, the system will generate a unique e-way bill number. This e-way bill can be downloaded or printed as proof of the transaction.
- Share with Transporter: The generated e-way bill must be carried with the goods during transport. The transporter is required to show the e-way bill when requested by authorities.
For more information on the e-way bill generation process, you can visit the official e-way bill portal: www.ewaybill.nic.in.
Latest Updates on E-Way Bill
- Mandatory E-Way Bill for Specific Goods: As per recent amendments, specific goods like alcohol, hazardous chemicals, and certain food items now require e-way bills even for intra-state transportation. (Source: GST Council).
- Multiple E-Way Bill Generation: In case goods are being transported in multiple vehicles, individual e-way bills must be generated for each vehicle, though businesses can consolidate details for easier management.
- Validity Period for E-Way Bill: The validity period of an e-way bill depends on the distance covered. For example, if the distance to be covered is up to 100 km, the e-way bill is valid for one day. For every additional 100 km, one extra day is allowed.
- E-Way Bill for Return of Goods: If goods are being returned due to quality issues or for any other reason, businesses need to generate a new e-way bill for the return shipment.
- New Format for E-Way Bill: The government has recently updated the e-way bill format to make it more user-friendly and comprehensive. This update includes additional fields for better tracking and data analysis.
P.C. – cleartax.in
The Role of GSTIN Check in E-Way Bill Generation
An essential part of generating an e-way bill involves verifying the GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number) of both the sender and recipient. The GSTIN check ensures that the parties involved are registered under the GST regime and that the transaction complies with the tax rules. You can check GSTIN details online on various official government platforms to verify its authenticity before generating the e-way bill.
To perform a GSTIN check, visit the GST portal: https://www.gst.gov.in.
Key Features of the E-Way Bill Portal (www.ewaybill.nic.in)
The e-way bill portal is designed to be simple to use while maintaining a high level of compliance and security. Some of its key features include:
- User-Friendly Interface: The portal offers a user-friendly interface that allows easy navigation for both businesses and transporters.
- Real-Time Tracking: It provides real-time tracking of goods and their respective e-way bill status.
- E-Way Bill Consolidation: The system allows businesses to consolidate multiple e-way bills into a single document, easing the documentation process.
- Multi-Language Support: The portal is available in multiple languages to cater to users from different states.
- Notifications: The portal sends notifications regarding the status of the e-way bill to help businesses stay updated.
For more details about how the portal works, you can visit www.ewaybill.nic.in.
FAQs about E-Way Bill Limit
1. What is the e-way bill limit for interstate transportation? The e-way bill must be generated if the value of goods exceeds ₹50,000 for interstate transportation.
2. Do I need an e-way bill for intra-state transportation? Yes, e-way bills may be required for intra-state transportation if the value exceeds ₹50,000, depending on the state’s regulations.
3. Can I generate multiple e-way bills for a single consignment? Yes, if goods are being transported by multiple vehicles, separate e-way bills must be generated for each vehicle.
4. How do I check if my GSTIN is valid? You can check the validity of your GSTIN through the official GST portal at https://www.gst.gov.in.
5. Is there a time limit for generating an e-way bill? An e-way bill should be generated before the movement of goods. Failure to do so can lead to penalties.
6. What is the validity period of an e-way bill? The validity of an e-way bill depends on the distance. For distances up to 100 km, it is valid for one day, and for each additional 100 km, one extra day is allowed.
7. Can e-way bills be generated for exempted goods? No, e-way bills are not required for goods that are exempt from GST.
8. What happens if the e-way bill is not generated? If the e-way bill is not generated, the goods may be detained, and penalties may be imposed.
9. How can I check the status of my e-way bill? You can check the status of your e-way bill on the official e-way bill portal at www.ewaybill.nic.in.
10. Are there any penalties for not generating an e-way bill? Yes, failure to generate an e-way bill can result in penalties, including fines and detention of goods.
Conclusion
The e-way bill system is a critical component of the GST structure in India. It helps businesses comply with the law, facilitates smooth interstate and intrastate goods movement, and reduces the chances of tax evasion. Understanding the e-way bill limit and the process for its generation is crucial for businesses and transporters involved in the movement of goods. With the latest updates and improvements to the system, the government is continually working to make the process more efficient and user-friendly.
For detailed information, you can visit the official government websites: www.ewaybill.nic.in and https://www.gst.gov.in.
Also Read: Understanding ESI Contribution in India: A Complete Guide
Also Read: New Education Policy 2024: Transforming India’s Education Landscape
Also Read: Complete Guide on GST ARN Status: All You Need to Know
Also visit: Online Legal Service, Virtual Advice and Consultation



